Tibial Interlocking Nail Tips for Faster Recovery and Healing?
Tibial Interlocking Nail technology has significantly advanced orthopedic surgery. This method is designed to stabilize fractures in the tibia, a vital bone in our leg. Speedier recovery is often a priority for patients. With the right techniques, outcomes can improve dramatically.
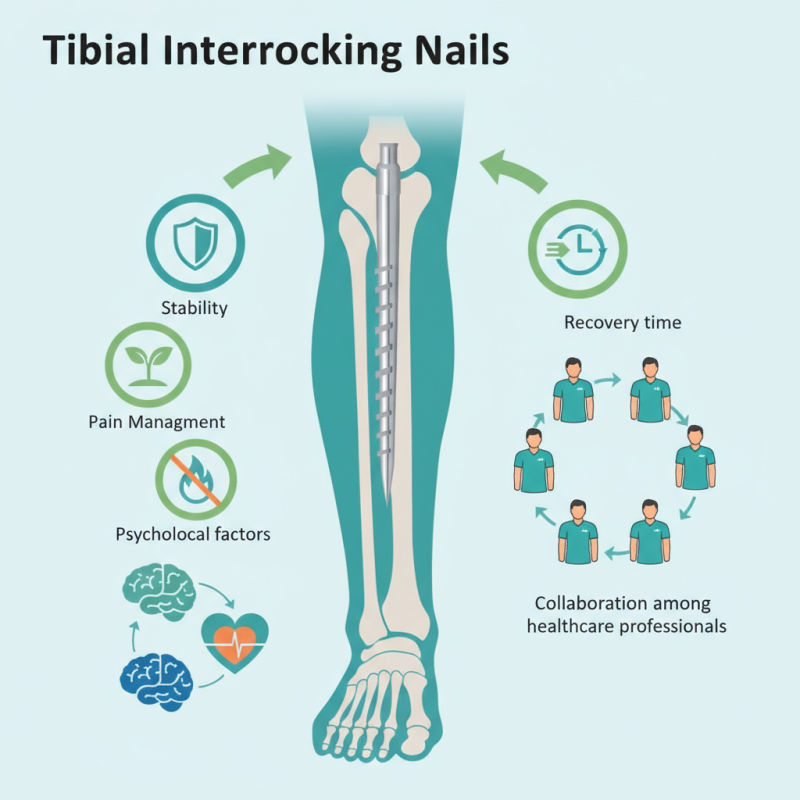
Surgeons have noted several advantages of using the Tibial Interlocking Nail. It provides strong stability and reduces the risk of malunion. However, as with any procedure, it is not without its challenges. Complications can arise, affecting recovery times.
Many patients report increased pain during recovery. Psychological factors also play a role. Understanding these nuances is crucial for achieving better results. Collaboration among healthcare professionals can enhance the effectiveness of this method. A thorough discussion can lead to refined approaches and improved recovery experiences.
Understanding Tibial Interlocking Nails and Their Functionality
Tibial interlocking nails are crucial for stabilizing fractures in the tibia. These metal rods provide internal support, allowing bones to heal properly. This method promotes faster recovery due to enhanced stability during the healing process. The nails are inserted through the skin, minimizing the need for extensive surgical procedures.
Tips for optimal recovery:
Adhering to a consistent rehabilitation program is key. Gradual weight-bearing exercises help strengthen muscles and joints. Nutrition plays a vital role too; consuming adequate protein and calcium supports bone health. Stay hydrated, as fluids boost circulation, which aids healing.
It’s essential to recognize the challenges that come with recovery. Patients may experience pain or discomfort. Regular communication with healthcare providers is necessary. Reflecting on personal progress can foster resilience. Keeping a journal of physical limitations and milestones can motivate individuals through their healing journey.
The Surgical Procedure: Insertion of Tibial Interlocking Nails
The surgical procedure for inserting tibial interlocking nails is quite meticulous. Surgeons begin by making a small incision near the knee. This opening allows access to the femur. The aim is to align the nail accurately within the bone. Operators often use fluoroscopy to guide the insertion. This imaging helps ensure precise placement. Everything must be perfect for stability and healing.
Once the nail is in place, holes are drilled through the nail and into the bone. This secures the nail in position. Additional screws may be placed to enhance stability. The entire process requires patience and skill. Recovery can be quicker, but not without challenges. Patients may experience discomfort post-surgery. Physical therapy is crucial for regaining strength. The road to recovery varies for everyone.
While the procedure is effective, it is not flawless. Some patients face complications like infection. These risks must be managed carefully. Each case demands close monitoring. Surgeons must communicate thoroughly with their teams. They need to be prepared for unexpected scenarios. Reflecting on the technique can lead to improvements in practice. The journey doesn't end once the nail is in. Healing is a continuous process.
Benefits of Tibial Interlocking Nails for Bone Healing
Tibial interlocking nails offer significant advantages for bone healing. Studies indicate that these nails can reduce healing time by as much as 20%. The mechanical stability they provide is crucial for the early mobilization of patients. With faster recovery, many patients return to daily activities sooner. This can greatly improve their quality of life post-surgery.
Research highlights that the use of tibial interlocking nails minimizes complications. One report shows a decrease in non-union rates to around 5%. This is vital for patients since untreated non-unions can lead to prolonged pain and a lengthy rehabilitation process. However, some challenges remain. Surgeons need to properly align and secure the nails to avoid complications. Misalignment can lead to increased recovery times and the necessity for additional surgeries.
Patient factors also play a role in healing. Age, nutrition, and overall health all influence recovery outcomes. For instance, older patients may experience slower healing. Therefore, while tibial interlocking nails provide many benefits, individual circumstances must be considered. Ongoing research is necessary to further refine techniques and improve patient outcomes. The goal is to make recovery not just faster, but also safer and more effective.
Post-Operative Care: Enhancing Recovery with Tibial Nails
Post-operative care plays a crucial role in recovering from tibial nail surgery. The key to a successful recovery is understanding how to manage pain and promote healing. Studies indicate that proper post-operative care can reduce recovery time by 20-30%. A comprehensive approach includes medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle adjustments.
Physical therapy should begin as soon as possible. Gentle exercises are vital. Engaging in range-of-motion activities can help improve circulation and reduce stiffness. According to recent data, patients who start therapy within a week of surgery experience faster bone healing. They also report higher satisfaction levels. Regular follow-ups with medical professionals ensure that healing is progressing effectively.
Nutrition cannot be overlooked. A balanced diet rich in protein and vitamins accelerates tissue repair. Research shows that vitamin D and calcium are essential for bone health. However, many patients do not prioritize their diet during recovery. This oversight may prolong healing. Adequate hydration is equally important. Dehydration can hinder the healing process. Patients must stay aware of their body's needs. Listening to one’s body can prevent complications and undue delays in recovery. Each aspect requires attention and reflection for an optimal recovery journey.
Tibial Interlocking Nail Tips for Faster Recovery and Healing
| Dimension | Value |
|---|---|
| Average Recovery Time | 6-12 weeks |
| Pain Level (1-10 scale) | 3-5 |
| Average Hospital Stay | 2-4 days |
| Physical Therapy Duration | 4-6 weeks |
| Complication Rate | 5-10% |
| Patient Satisfaction Rate | 85-90% |
| Return to Daily Activities | 6-8 weeks |
Potential Risks and Complications of Tibial Interlocking Nailing
Tibial interlocking nailing is a common method for treating fractures. However, it comes with potential risks and complications. One significant concern is infection, which affects about 5-10% of patients. This risk increases if proper hygiene is not maintained during the procedure.
Delayed union or non-union is another complication. Research shows that around 15% of tibial fractures may not heal properly. Factors like patient age and overall health contribute to this issue. Surgeons often need to assess the stability of the fracture carefully.
Nerve or vascular injury is also possible. Studies indicate that these injuries can occur in up to 2% of cases. Such complications can lead to long-term repercussions for the patient. It's crucial for medical professionals to weigh the benefits against these risks before proceeding.